The Aging Population: Challenges and Opportunities for Aging Societies
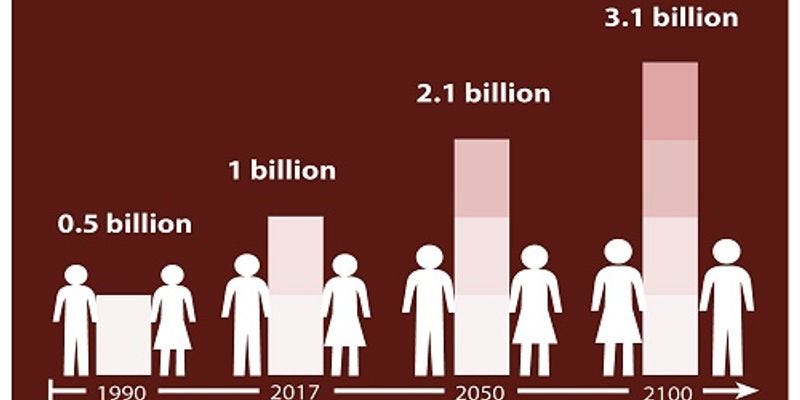
As the world’s population continues to age, societies across the globe are facing a profound demographic shift.
While this aging trend presents unique challenges, it also offers a host of opportunities. In this article, we explore the challenges and opportunities associated with an aging population and the strategies that can help societies navigate this transformation successfully.
The Aging Trend
Population aging is the result of declining birth rates and increasing life expectancy. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), by 2050, one in six people worldwide will be over the age of 65. This shift poses several significant challenges:
1. Healthcare: Aging populations often require more extensive and specialized healthcare services, which can strain healthcare systems.
2. Economic Impact: A smaller working-age population can lead to economic challenges, including increased pension and healthcare costs.
3. Social Support: Providing adequate social support for elderly citizens becomes more critical as their numbers grow.
4. Ageism: Combatting ageism and ensuring that older adults are treated with dignity and respect is an ongoing challenge.
The Silver Lining: Opportunities in Aging
While population aging presents challenges, it also offers opportunities for societies:
1. Experienced Workforce: Older individuals can contribute to the workforce with their experience and expertise, potentially mitigating labor shortages.
2. Innovation: Aging societies can drive innovation in healthcare, technology, and services catering to older adults’ needs.
3. Social Capital: Older adults often have strong social networks, which can foster social cohesion and support within communities.
4. Knowledge Transfer: Older generations can pass down valuable knowledge and traditions to younger ones.
Strategies for Success
To harness the potential benefits of an aging population while addressing its challenges, societies can implement several key strategies:
1. Healthcare Innovation: Invest in healthcare innovations that promote healthy aging, disease prevention, and improved access to care for older adults.
2. Flexible Retirement: Encourage flexible retirement options that allow older adults to remain in the workforce if they wish and gradually transition into retirement.
3. Lifelong Learning: Promote lifelong learning opportunities to keep older adults engaged, mentally active, and prepared for the workforce.
4. Social Inclusion: Create age-friendly communities that combat isolation and foster social inclusion for older residents.
5. Pension Reforms: Implement sustainable pension and retirement systems that address the financial challenges of an aging population.
6. Health Promotion: Promote healthy lifestyles and preventive healthcare measures to reduce the burden of chronic diseases in older age.
The aging population is not a crisis but rather a transformative demographic shift that offers both challenges and opportunities.
To navigate this change successfully, societies must adopt a proactive and inclusive approach.
By investing in healthcare, promoting lifelong learning, fostering social inclusion, and creating age-friendly communities, societies can ensure that their aging populations continue to contribute to the well-being and prosperity of all members.
Embracing the potential of older adults is not only essential for their dignity and quality of life but also for the vitality and sustainability of aging societies.
