Basic Strings (Python From Zero To One — Part 18)
Day 88 of experimenting with video content
Intro to Strings
a = 'hello world'
b = "apple pie"We can think of strings as a sequence of characters, and we use either single or double quotes (both works) to define strings. Here, a is a string, and b is also a string.
String addition & multiplication
a = 'apple'
b = 'pie'
print(a + b) # applepie
print(b + a) # pieapple^ adding strings joins them together (order matters)
a = 'apple'
print(a * 3) # appleappleapple^ multiplying a string with an integer n joins n of the string together.
Note — a string can only be added with another string, and a string can only be multiplied with an integer. We get errors if we try anything else.
Compound assignment operators
a = 'apple'
a += 'pie'
print(a) # applepie^ a += 'pie' means we add 'pie' to the back of a
a = 'apple'
a *= 3
print(a) # appleappleapple^ a *= 3 means we multiply a by 3
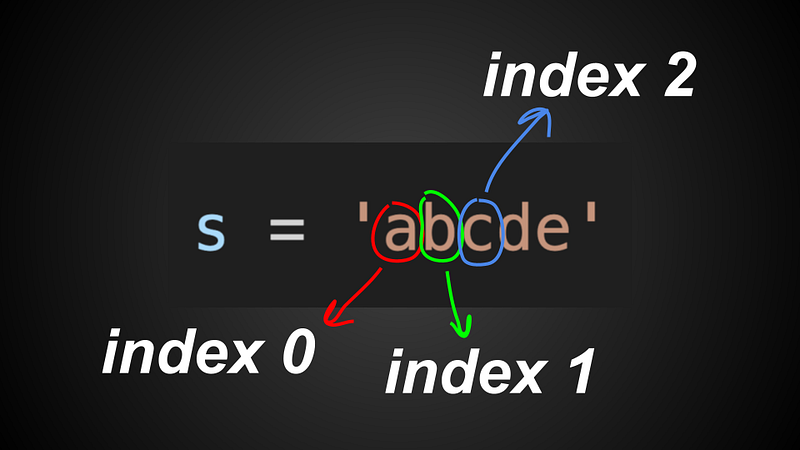
Basic indexing
string = 'abcde'
print(string[0]) # a
print(string[1]) # b
print(string[2]) # c
print(string[3]) # d
print(string[4]) # eWhen we index a string eg. string[n] where n is an integer, we are actually getting the character at that certain index n.
In Python, we start counting from 0, so the index of our first character a would be 0.
- index of
ainabcdeis 0 - index of
binabcdeis 1 - index of
cinabcdeis 2 - index of
dinabcdeis 3 - index of
einabcdeis 4
Index out of range error
string = 'abcde'
print(string[0]) # a
print(string[1]) # b
print(string[2]) # c
print(string[3]) # d
print(string[4]) # e
print(string[5]) # index out of range errorif we attempt to index a character that isn’t there, we get an index out of range error. Here in the string abcde, we only have characters up til index 4 (5th position) — if we try to index 5, we just get an error.
Negative indexes
string = 'abcde'
print(string[-1]) # e
print(string[-2]) # d
print(string[-3]) # c
print(string[-4]) # b
print(string[-5]) # aWhen we pass in negative indexes when doing string indexing, we start counting from the right instead of the usual left side.
eis at index-1dis at index-2cis at index-3bis at index-4ais at index-5
Which can be useful if we are dealing with characters nearer to the right end of our string.
string = 'abcde'
print(string[-1]) # e
print(string[-2]) # d
print(string[-3]) # c
print(string[-4]) # b
print(string[-5]) # a
print(string[-6]) # index out of range error^ similarly, if we attempt to use a negative index that doesn’t exist in the string, we will just get an index out of range error.
Conclusion
Hope this was clear and easy to understand.
Some Final words
If this story was helpful and you wish to show a little support, you could:
- Clap 50 times for this story
- Leave a comment telling me what you think
- Highlight the parts in this story that resonate with you
These actions really really help me out, and are much appreciated!
Ebooks I’ve Written: https://zlliu.co/ebooks
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/zlliu/





