AWS VPC Peering vs. AWS Transit Gateway
Connecting Networks in the Cloud
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides multiple solutions for connecting virtual private clouds (VPCs) and on-premises networks, but two commonly used options are VPC peering and AWS Transit Gateway.

In this article, we will explore these two connectivity solutions, compare their features, and help you decide which one is the right fit for your specific networking requirements.
AWS VPC Peering
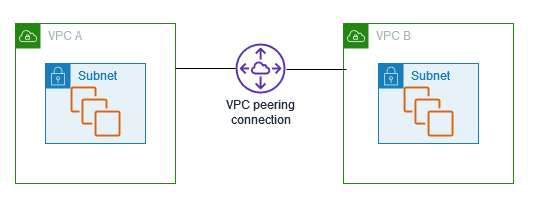
VPC peering creates a direct, Point-to-Point Connection between two VPCs, allowing them to communicate as if they were on the same network.
- Simple and Cost-Effective
VPC peering is straightforward to set up and cost-effective. It’s ideal for scenarios where you need to connect a few VPCs, such as different environments of a single application. And you just need to pay for the data transfer.
- Low Latency and No Bandwidth Bottleneck
Since VPC peering operates at the network level, it offers low-latency communication between peered VPCs. As it does not rely on a separate piece of physical hardware so there is no single point of failure for communication or a bandwidth bottleneck.
VPC peering is limited to connecting two VPCs at a time. For complex architectures with multiple VPCs, you’ll need to establish separate peering connections, potentially leading to management overhead. At the same time, you need to configure and manage multiple route tables for your complex network. So, that’s why AWS Transit Gateway comes out…
AWS Transit Gateway
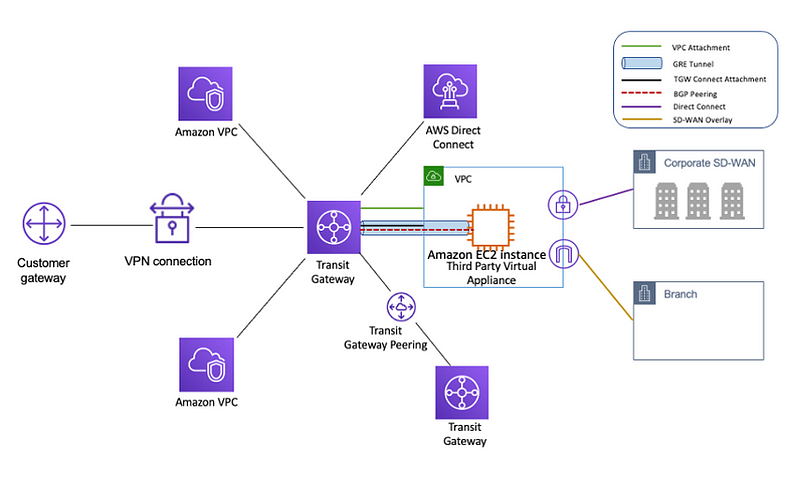
AWS Transit Gateway acts as a hub for connecting multiple VPCs and on-premises networks, simplifying the overall network architecture.
- Scalability
Transit Gateway can connect up to thousands of VPCs, making it suitable for large and complex environments.
- Simplified Route Propagation
Transit Gateway propagates routes automatically to connected VPCs, reducing the need for manual configuration.
- Network Segmentation
It allows for network segmentation and routing isolation, making it easier to manage and secure different parts of your network.
However, Transit Gateway is not suitable for all use cases:
- While Transit Gateway simplifies network architecture for complex setups, it can be overkill for smaller, simpler environments.
- AWS charges for data transfer across Transit Gateway, which means there may be additional costs, especially in scenarios with high data transfer rates.
Choose the Right Solution For Your Network
VPC Peering:
- Choose VPC peering when you have a few VPCs that need to communicate, and you require low-latency connections.
- It’s a straightforward, cost-effective solution for simple scenarios.
AWS Transit Gateway:
- Opt for AWS Transit Gateway when you have a complex network that spans multiple VPCs and potentially includes on-premises data centres.
- It simplifies network management and scales effectively to meet the needs of large, multi-VPC architectures.
Finally
Hope this is helpful for you. And please follow me if you are interested in Cloud, DevOps, automation, programming, and any tech topics. I would also appreciate it if you could give me a clap.
Your comments are always welcome.
Thanks.
Harry@NZ
Thank you for being a part of our community! Before you go:
- Be sure to clap and follow the writer! 👏
- You can find even more content at PlainEnglish.io 🚀
- Sign up for our free weekly newsletter. 🗞️
- Follow us on Twitter(X), LinkedIn, YouTube, and Discord.




